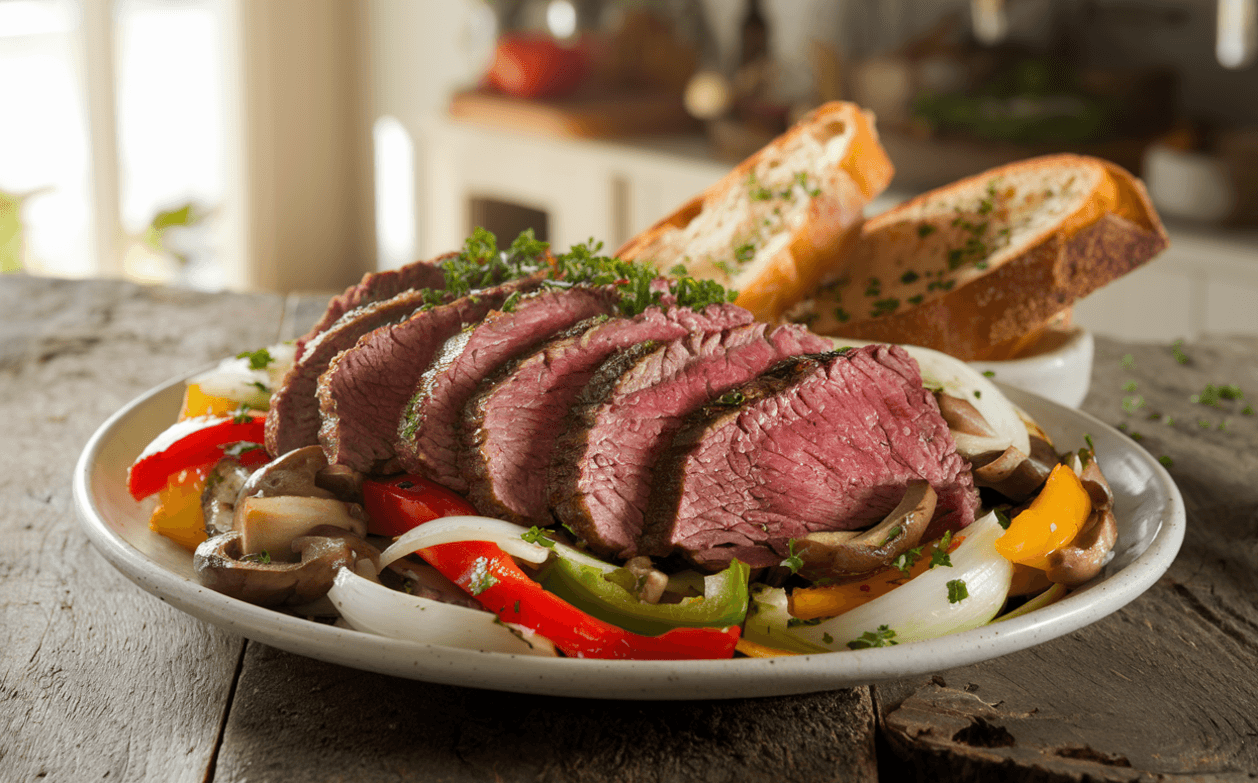A Complete Guide to Delicious and Easy Dishes
Shaved beef is a versatile ingredient that offers endless possibilities in the kitchen. Whether you’re preparing a quick weeknight dinner or an elaborate meal for guests, its thin, tender slices cook quickly and absorb flavors beautifully. This article explores a range of shaved beef recipes, tips, and techniques to make the most out of this flavorful cut.
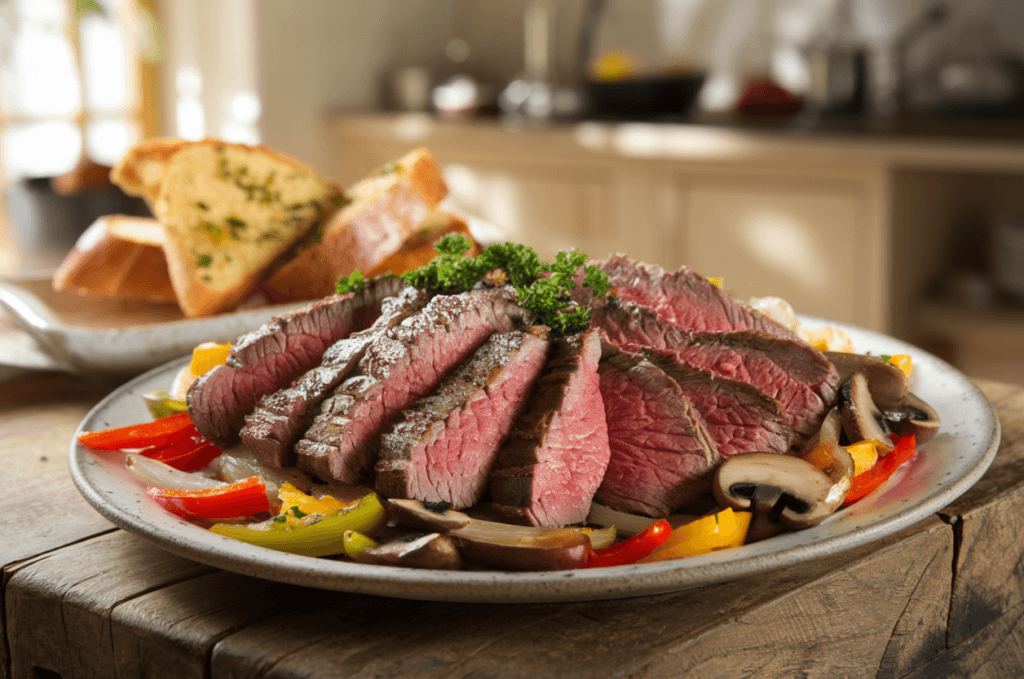
Shaved Beef Stir-Fry with Vegetables
Preparation Information
- Preparation Time: 15 minutes
- Cooking Time: 15 minutes
- Servings: 4
- Total Time: 30 minutes
- Cooking Method: Sautéed in a wok or large skillet over medium-high heat.
Ingredients
- 300 g (10 oz) shaved beef
- 1 red bell pepper, thinly sliced
- 1 yellow bell pepper, thinly sliced
- 1 onion, thinly sliced
- 150 g (5 oz) mushrooms, sliced
- 2 garlic cloves, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tbsp oyster sauce (optional)
- 1 tsp fresh ginger, grated
- 1 tbsp vegetable oil (sunflower or peanut oil)
- 1 tbsp toasted sesame seeds (optional)
- Salt and pepper to taste
- 2 tbsp fresh parsley or cilantro, chopped (for garnish)
Instructions
Step 1: Prepare the Ingredients
Slice all vegetables and ensure the shaved beef is fully thawed if frozen. Mix the soy sauce, oyster sauce (if using), grated ginger, and garlic in a small bowl for easy access during cooking.
Step 2: Heat the Wok
Heat the vegetable oil in a wok or large skillet over medium-high heat until it shimmers.
Step 3: Sear the Beef
Add the shaved beef in a single layer and let it sear for 2-3 minutes without stirring to develop a golden crust. Stir quickly, then remove the beef from the pan and set it aside.
Step 4: Cook the Vegetables
Add a bit more oil to the pan if needed. Toss in the garlic and ginger, cooking for 30 seconds until fragrant. Add the sliced bell peppers, onion, and mushrooms. Stir-fry for 4-5 minutes until the vegetables are slightly tender but still crisp.
Step 5: Combine the Beef and Vegetables
Return the seared beef to the pan. Pour in the soy sauce mixture and stir well to coat everything. Cook for another 2 minutes, allowing the flavors to meld.
Step 6: Final Touches
Taste and adjust seasoning with salt and pepper if needed. Sprinkle with toasted sesame seeds and garnish with fresh parsley or cilantro before serving.
Nutritional Information (Per Serving)
- Calories: 250
- Fat: 12 g
- Carbohydrates: 12 g
- Protein: 22 g
Enjoy this quick and nutritious dish!
Nutritional Value: Unlocking the Power of Food for Better Health
Nutritional value is at the heart of understanding how the foods we eat impact our health. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the concept, its components, and practical ways to optimize it in daily life.
Understanding Nutritional Value
Definition and Importance
The term “nutritional value” refers to the content of essential nutrients and calories found in food. It plays a critical role in determining how a particular food contributes to your health and energy needs.
Why Is It Important?
- Proteins aid muscle repair and growth.
- Carbohydrates provide energy.
- Fats support cellular health and brain function.
- Vitamins and minerals ensure overall body functionality, from bone health to immune support.
Failing to consider nutritional value can lead to deficiencies, low energy, or long-term illnesses.
Components of Nutritional Value
Macronutrients
- Proteins: Found in beans, meats, and dairy, they are the building blocks of life.
- Carbohydrates: Present in grains and fruits, they supply energy quickly.
- Fats: Healthy fats from nuts and fish promote cognitive function and maintain cellular health.
Micronutrients
- Vitamins: A, C, D, and others support immunity and bone strength.
- Minerals: Calcium, iron, and magnesium are essential for critical processes.
Measuring Nutritional Value
- Caloric Content: Represents the energy a food provides.
- Nutrient Density: Evaluates how rich a food is in essential nutrients relative to its calorie count.
Foods like leafy greens and berries are high in nutrient density, making them excellent choices for a balanced diet.
Nutritional Value of Common Foods
- Fruits and Vegetables: Abundant in vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Provide complex carbohydrates and essential minerals.
- Dairy and Alternatives: Excellent sources of calcium and protein.
- Meats and Seafood: Supply proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins.
Selecting a variety from these groups ensures a well-rounded intake of nutrients.
Nutritional Value and Food Labels
Understanding food labels is crucial for gauging nutritional value. Labels display serving sizes, calorie content, and nutrient percentages.
Beware of Misleading Terms
- “Low-fat”: May contain added sugars for taste.
- “Organic”: While often fresher, not always higher in nutrients.
Always review ingredient lists to make informed decisions.
Factors Affecting Nutritional Value
- Cooking Methods: Steaming or roasting preserves nutrients better than boiling.
- Storage: Frozen produce retains nutrients longer than improperly stored fresh items.
- Processing: Highly processed foods often lose nutritional integrity.
Nutritional Value and Diets
Examples of Diets
- Mediterranean Diet: Prioritizes healthy fats and plant-based foods.
- Ketogenic Diet: Focuses on fats and minimizes carbs.
Understanding nutritional needs can help you adapt these diets to fit personal health goals.
Myths and Misconceptions About Nutritional Value
Not all health claims about foods hold up under scrutiny:
- “Low-fat” doesn’t always mean healthier.
- Not all “superfoods” are inherently better than traditional counterparts.
Education and critical thinking are vital to navigating these claims.
Enhancing Nutritional Value in Meals
Boosting nutritional value is simple:
- Use fresh ingredients.
- Combine foods (e.g., vitamin C-rich fruits with iron-rich spinach).
- Swap refined grains for whole grains.
Seasonal and Local Foods’ Nutritional Value
Seasonal and locally grown foods often have higher nutritional value because they are fresher and less processed.
Example: Tomatoes picked in season are richer in flavor and nutrients.
Technological Advances in Understanding Nutritional Value
Advances like nutrigenomics (genes influencing nutrition) and smartphone apps help personalize diets and track nutritional intake more effectively.
Global Perspectives on Nutritional Value
Different cuisines showcase diverse approaches to nutrition:
- Asian diets: Emphasize rice and vegetables.
- Mediterranean diets: Focus on olive oil and seafood.
Exploring these approaches can inspire healthier eating habits.
The Role of Nutritional Value in Preventing Diseases
Nutrient-rich foods can prevent chronic conditions:
- Fiber-rich diets: Lower heart disease risk.
- Antioxidants: Aid in cancer prevention.
Evaluating Nutritional Value for Special Populations
- Children: Need high protein and calcium for growth.
- Pregnant Women: Benefit from folic acid and iron.
- Elderly Individuals: Require vitamin D and calcium for bone health.
Future of Nutritional Value Studies
Exciting developments like personalized diets and AI-driven health tracking are shaping the future of nutrition science.
FAQs About Nutritional Value
What is the best way to maximize nutritional value in cooking?
Steaming or roasting preserves nutrients better than boiling.
How can I tell if a food is nutrient-dense?
Choose whole, minimally processed foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
Do organic foods have higher nutritional value?
Organic foods are often fresher but not always significantly higher in nutrients.
A Guide to Delicious and Versatile Cuts
Shaved beef is a versatile ingredient beloved in kitchens worldwide, from sizzling stir-fries to classic Philly cheesesteak sandwiches. This article will guide you through the essentials of choosing the best shaved beef to ensure your meals are both flavorful and nutritious.
What is Shaved Beef?
Shaved beef refers to thinly sliced cuts of beef, often used in recipes that require quick cooking. Its tender texture and ability to absorb flavors make it a favorite for dishes like beef stir-fries, tacos, and wraps. Shaved beef is typically sliced from various cuts, each offering unique qualities suited to different cooking styles.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Shaved Beef
Selecting the best shaved beef requires attention to detail. Here are the main factors to keep in mind:
- Cut Quality: Opt for cuts known for their tenderness and flavor, like ribeye or sirloin.
- Freshness: Look for beef with a bright red color and minimal liquid in the packaging.
- Texture and Color: Avoid beef with a slimy texture or grayish discoloration, as these indicate poor quality.
Popular Cuts Used for Shaved Beef
The quality of shaved beef often depends on the cut it’s sourced from. Common choices include:
- Ribeye: Renowned for its marbling and rich flavor, ideal for cheesesteaks.
- Sirloin: A leaner cut, perfect for stir-fries and lighter recipes.
- Brisket: Offers a hearty flavor, excellent for slow-cooked dishes.
- Flank Steak: Known for its chewiness but can be tender when sliced thin.
Fresh vs. Frozen Shaved Beef
Fresh shaved beef is often preferred for its flavor and texture, but frozen options can be just as good when handled properly. Frozen shaved beef retains nutrients and can be convenient for storage, especially if you’re buying in bulk. When choosing frozen, ensure the packaging is sealed tight and free of ice crystals, which may indicate freezer burn.
Grass-Fed vs. Grain-Fed Shaved Beef
Grass-fed beef typically has a deeper, earthier flavor and is higher in omega-3 fatty acids. Grain-fed beef, on the other hand, offers a milder flavor and higher marbling. Both are excellent options, but your choice may depend on dietary preferences and ethical considerations.
Choosing Shaved Beef Based on Cooking Methods
Different recipes may call for specific types of shaved beef:
- Stir-Frying: Lean cuts like sirloin work best due to their quick cooking time.
- Grilling: Ribeye or marinated flank steak brings out smoky flavors.
- Pan-Frying: Thinly shaved brisket can develop a crispy texture.
Packaging and Storage Considerations
Packaging plays a critical role in maintaining the quality of shaved beef. Vacuum-sealed packaging extends shelf life by preventing exposure to air and contaminants. If you’re storing shaved beef, refrigeration is ideal for short-term use, while freezing is best for longer periods. Always label and date your packages to track freshness.
Nutritional Value of Shaved Beef
Shaved beef is not only flavorful but also nutritionally rich. It’s an excellent source of protein, providing about 20–25 grams per serving. Additionally, it contains essential vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and B vitamins. For those monitoring fat intake, lean cuts like sirloin are a great choice.
How to Identify High-Quality Shaved Beef in Stores
When shopping for shaved beef, consider these tips to ensure quality:
- Color: Fresh beef should be bright red. Avoid beef with grayish hues.
- Marbling: Fine white streaks of fat enhance flavor and tenderness.
- Smell: A fresh, neutral smell is ideal. A sour odor indicates spoilage.
Buying Shaved Beef Online
Online meat vendors can offer premium shaved beef options, often sourced directly from farms. Ensure the vendor provides clear details about the cut, origin, and packaging. Look for proper insulation and expedited shipping to maintain freshness during transit.
Common Uses for Shaved Beef in Recipes
Shaved beef is a versatile ingredient that enhances many dishes:
- Philly Cheesesteak Sandwiches: Combine ribeye with melted cheese and sautéed onions.
- Asian Stir-Fries: Use thin strips of sirloin with soy sauce, garlic, and vegetables.
- Tacos and Wraps: Add shaved beef, avocado, and salsa for a quick, flavorful meal.
Shaved Beef Alternatives for Special Diets
For those seeking alternatives, consider plant-based meat substitutes made from soy or pea protein. These mimic the texture of shaved beef and work well in recipes. For lower-fat options, turkey or chicken breast can be shaved and seasoned to taste.
Budget-Friendly Options for Shaved Beef
Cuts like chuck roast or bottom round are affordable yet flavorful when shaved thin. Buying in bulk and shaving the beef at home can also save money. Local butcher shops often provide customized cuts at a lower cost than prepackaged options.
Ethical and Sustainable Sourcing
Sustainably raised beef not only supports the environment but also ensures better quality. Look for certifications like USDA Organic, Certified Humane, or Grass-Fed when shopping. These labels indicate higher standards in animal welfare and environmental impact.
Tips for Storing and Freezing Shaved Beef at Home
To store shaved beef:
- Refrigerate: Use within 2–3 days to maintain freshness.
- Freeze: Wrap tightly in plastic wrap or use vacuum-sealed bags. Avoid freezer burn by double-wrapping.
Frozen shaved beef can last up to six months if stored properly.
FAQs About Choosing the Best Shaved Beef
What is the best cut for shaved beef? Ribeye is ideal for flavor and tenderness, but sirloin is a leaner option.
How do I store shaved beef for the longest shelf life? Vacuum-sealing and freezing are best for long-term storage.
Can I use frozen shaved beef for stir-fries? Yes, thaw it in the refrigerator for best results.
Is grass-fed beef worth the extra cost? It often has better nutritional value and ethical benefits.
How can I tell if shaved beef is fresh? Check for bright red color, firm texture, and a neutral smell.
Can I shave beef at home? Yes, partially freeze the meat for easier slicing with a sharp knife or meat slicer.
Essential Tools for Cooking I
A Guide to Mastering Culinary Techniques
Cooking is an art that transforms raw ingredients into delightful dishes. Choosing the right cooking method can enhance flavor, texture, and nutrition. In this article, we’ll explore the most popular cooking methods, their applications, and how to master them.
Understanding Cooking Methods
Cooking methods are techniques used to prepare food by applying heat. Selecting the right method depends on the type of ingredient, desired texture, and flavor profile. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced cook, understanding various techniques can elevate your culinary skills.
Dry Heat Cooking Methods
Dry heat cooking involves cooking food without added liquid or moisture. It uses high temperatures to caramelize the natural sugars in food, creating rich flavors.
- Baking: Ideal for bread, cakes, and casseroles, baking uses consistent, dry heat in an oven.
- Roasting: A favorite for meats and vegetables, roasting adds a crispy exterior while keeping the inside tender.
- Grilling: High heat from below chars the food, creating a smoky, distinct flavor. Perfect for steaks and burgers.
- Broiling: Similar to grilling but applies heat from above, broiling is great for melting cheese or quickly cooking fish.
Moist Heat Cooking Methods
Moist heat cooking uses water, broth, or steam as the primary medium to cook food. It’s excellent for tenderizing and preserving delicate flavors.
- Boiling: Submerging food in boiling water is efficient for cooking pasta and vegetables.
- Simmering: A gentler version of boiling, simmering is ideal for soups and sauces.
- Steaming: A healthy option that uses steam to cook without removing nutrients, often used for vegetables and seafood.
- Poaching: Gently cooking food in liquid at low temperatures, perfect for eggs and delicate fish.
Combination Cooking Methods
Combination cooking methods blend dry and moist heat to create complex flavors and tender textures.
- Braising: Involves searing food at high heat, then cooking it slowly in liquid. Popular for tougher cuts of meat.
- Stewing: Similar to braising but uses smaller pieces of meat or vegetables submerged in liquid.
Popular Cooking Methods for Meats
Cooking meat to perfection requires an understanding of its texture and fat content. Grilling is ideal for tender cuts like steaks, while slow cooking works wonders for tougher cuts like brisket. Roasting whole poultry ensures a crispy skin and juicy interior.
Popular Cooking Methods for Vegetables
Vegetables benefit from techniques that enhance their natural flavors. Sautéing brings out sweetness through caramelization. Steaming retains nutrients, while blanching preserves vibrant colors before further cooking.
Advanced Cooking Techniques
For those looking to experiment, advanced methods offer exciting opportunities:
- Sous Vide: Cooking vacuum-sealed food in a water bath at precise temperatures for consistent results.
- Molecular Gastronomy: Blends science and cooking to create unique textures, like foams or spheres.
- Smoking: Infuses food with deep, smoky flavors using wood chips.
Frying Techniques
Frying adds crispness and bold flavors to food. Different frying methods include:
- Deep Frying: Fully immerses food in hot oil, perfect for fries and doughnuts.
- Shallow Frying: Uses less oil and is ideal for items like fish fillets.
- Pan-Frying: Cooking food in a small amount of oil or fat, commonly used for meats.
- Stir-Frying: Quickly cooks bite-sized pieces of food in a hot pan, preserving crunch and color.
Cooking Methods for Healthy Eating
Health-conscious cooking focuses on techniques that minimize fat and retain nutrients. Steaming is excellent for preserving vitamins, while baking offers a low-fat alternative to frying. Grilling allows excess fat to drip away, making it another health-friendly option.
Cultural Influences on Cooking Methods
Cooking methods vary widely across cultures, reflecting geography and traditions. Asian cuisines favor stir-frying and steaming for quick, nutrient-rich meals. Mediterranean dishes often involve roasting and grilling, emphasizing natural flavors. Exploring these methods enriches culinary understanding.
Cooking Methods and Equipment
Each cooking method requires specific tools:
- Baking: Oven, baking sheets, and molds.
- Grilling: Charcoal or gas grills, tongs, and grill brushes.
- Sous Vide: Precision cooker and vacuum sealer.
Modern innovations like air fryers and instant pots have revolutionized traditional methods, combining convenience with efficiency.
Cooking Methods for Different Diets
Cooking methods can align with dietary goals. Low-fat diets benefit from steaming and baking, while high-protein diets emphasize grilling and pan-searing. Understanding dietary needs helps in selecting the most suitable techniques.
Pros and Cons of Popular Cooking Methods
Each method has strengths and limitations:
- Baking: Produces consistent results but requires time and precise measurements.
- Frying: Delivers bold flavors but adds calories from oil.
- Grilling: Infuses smoky flavor but may be less effective for tenderizing.
Choosing the right method depends on the dish and dietary preferences.
Choosing the Right Cooking Method for Ingredients
Selecting the right method enhances the natural qualities of ingredients. Meats often benefit from roasting or grilling, while vegetables shine when steamed or sautéed. Grains like rice and quinoa are best cooked through boiling or steaming.
FAQs About Popular Cooking Methods
What is the healthiest cooking method? Steaming retains the most nutrients and minimizes fat.
Can I use one method for all types of food? While possible, combining methods often yields better results.
What’s the easiest cooking method for beginners? Baking and steaming are simple and forgiving techniques.
How do I choose between frying and grilling? Frying offers richer flavors, while grilling is leaner and healthier.
Are modern gadgets worth it? Devices like air fryers and sous vide machines provide convenience and precision.
How do cooking methods impact flavor? Dry heat enhances caramelization, while moist heat preserves subtle flavors.
Popular Cooking Methods One of the best things about shaved beef is its versatility across cooking methods. Stir-frying is ideal for quick meals, grilling adds a smoky flavor, slow cooking ensures tenderness, and broiling can create a caramelized exterior.
Quick and Easy Shaved Beef Recipes If you’re in a hurry, shaved beef is your best friend. A simple stir-fry with soy sauce, garlic, and vegetables can be ready in under 15 minutes. Another option is beef quesadillas—just sauté shaved beef with onions and cheese, fold into a tortilla, and cook until golden.
Shaved Beef for Sandwiches Shaved beef shines in sandwiches, especially in the classic Philly cheesesteak. Thin slices of beef cooked with onions, green peppers, and provolone cheese, all served on a hoagie roll, make for an iconic meal. You can also try shaved beef with horseradish sauce in a baguette for a modern twist.
International Dishes with Shaved Beef Explore global cuisines with shaved beef. Make Korean bulgogi by marinating the beef in a mix of soy sauce, sesame oil, and sugar, then grilling it to perfection. For Mexican tacos, season the beef with chili powder and lime juice, then serve in corn tortillas with salsa and guacamole.
Comfort Food Recipes Nothing beats a hearty meal with shaved beef. Create a rich beef stew by simmering shaved beef with potatoes, carrots, and onions. Alternatively, try a cheesy beef casserole with layers of noodles, béchamel sauce, and shaved beef.
Healthy Shaved Beef Recipes For health-conscious eaters, shaved beef can be a guilt-free option. Toss it in a salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, and a vinaigrette. You can also try a stir-fry with shaved beef, broccoli, and cauliflower rice for a low-carb alternative.
Shaved Beef for Meal Prep Shaved beef is an excellent choice for meal prep. Cook a large batch with simple seasonings, then use it in various dishes throughout the week, such as salads, wraps, or rice bowls. Its quick-cooking nature saves time and effort.
Vegetable Pairings Pair shaved beef with vegetables that complement its flavor. Bell peppers, mushrooms, onions, and zucchini are excellent choices. Roasting or grilling these vegetables can enhance their natural sweetness and pair beautifully with the savory beef.
Common Mistakes to Avoid Avoid overcooking shaved beef, as its thin slices can become tough quickly. Marinating the beef beforehand helps tenderize it and adds flavor. Additionally, always preheat your cooking surface to ensure even cooking.
Storage and Leftovers Store leftover cooked shaved beef in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to three days. You can freeze uncooked shaved beef by wrapping it tightly to prevent freezer burn, ensuring it retains its texture and flavor.
FAQs
- What is shaved beef?
Shaved beef refers to thinly sliced cuts of beef, often used for quick-cooking recipes like stir-fries and sandwiches. - What cuts are used for shaved beef?
Common cuts include ribeye, sirloin, or flank steak, as they are tender and flavorful. - How long does it take to cook shaved beef?
Shaved beef cooks in just a few minutes, depending on the cooking method. - Can I use shaved beef in slow-cooked dishes?
Yes, but it’s better to add it toward the end of cooking to avoid overcooking. - What are some sauces that pair well with shaved beef?
Soy-based sauces, creamy horseradish, garlic butter, and BBQ sauce complement shaved beef perfectly. - Is shaved beef suitable for freezing?
Yes, you can freeze shaved beef either raw or cooked. Ensure it’s wrapped well to prevent freezer burn.
Conclusion Shaved beef is a culinary staple that combines versatility, flavor, and convenience. From quick stir-fries to hearty comfort food, there’s a recipe for every occasion. Try incorporating shaved beef into your meals for a delicious and satisfying protein source.